Hyperspectral payload
Spectral Response
Mark IV fleet hyperspectral payloads have a camera system which captures images with around 25m GSD and a swath width up to 145 km covering the wavelength ranges between 483 nm and 831 nm.
Below we can see differences in the spectral signature when compared with our multispectral imagery over the same area.
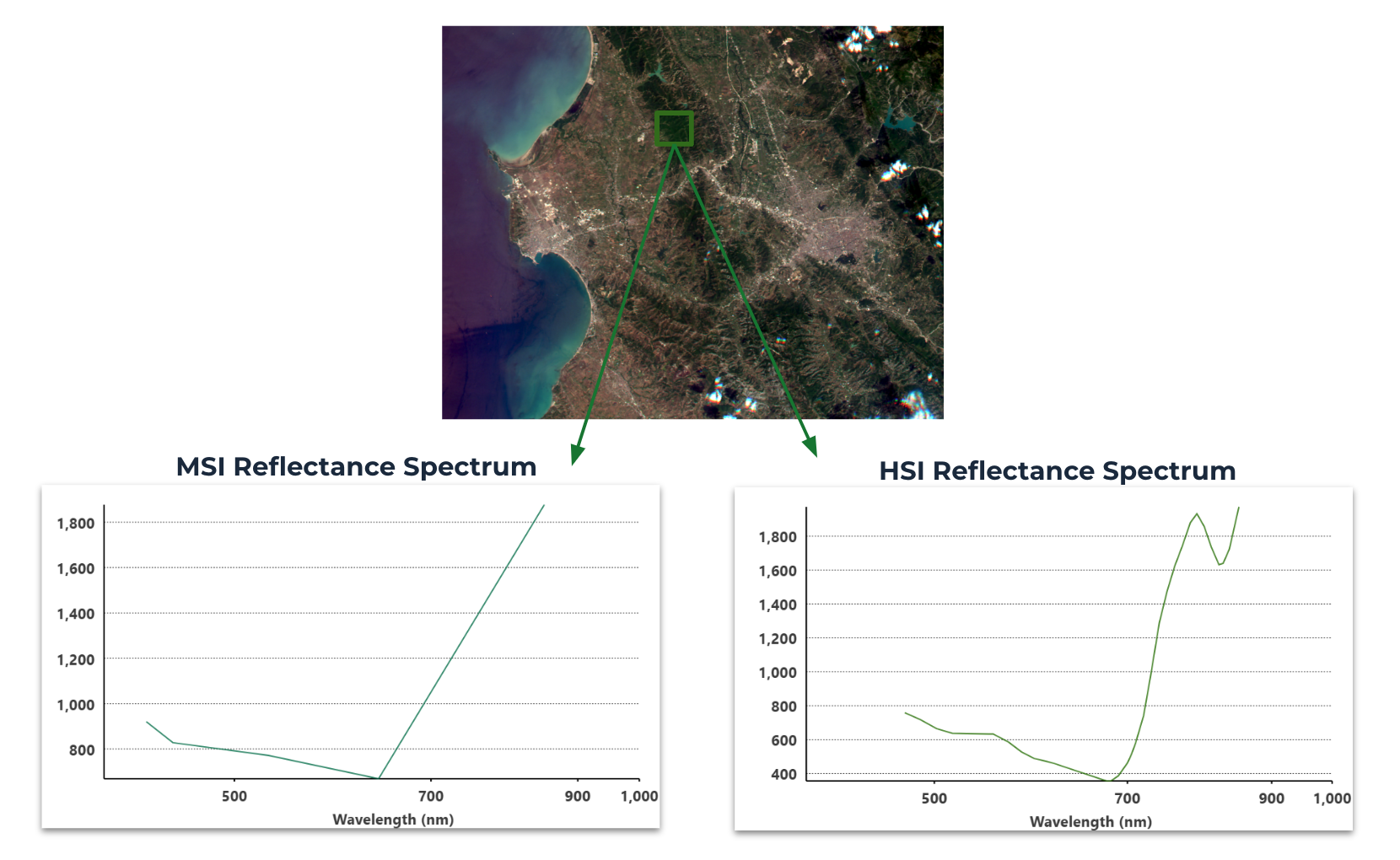
Imagery are captured in visible and near-infrared bands. In total, each capture consist of 32 bands:
- 483 nm (blue), 489 nm, 497 nm, 504 nm, 511 nm, 518 nm, 526 nm, 533 nm (green), 541 nm, 549 nm, 557 nm, 565 nm, 573 nm, 581 nm, 589 nm, 598 nm, 607 nm, 615 nm (red), 690 nm, 700 nm, 710 nm, 720 nm, 730 nm, 741 nm, 752 nm, 762 nm, 773 nm, 785 nm, 796 nm, 807 nm, 819 nm, 831 nm
Spatial Resolution
Satellogic's hyperspectral imagery products have a medium spatial resolution natively across all spectral bands. Images are captured with 25 meters native resolution at nadir for all spectral bands. Satellogic applies proprietary algorithms to enhance images on all bands providing considerable advantages in terms of pixel-level radiometry.
Radiometric Calibration
Satellogic imagery’s radiometric accuracy is attained through a combination of lab measurements and on-orbit vicarious calibrations. Satellogic performs on orbit calibration based on processing data retrieved from crossovers with a well calibrated source. The main target used for vicarious campaigns is El Borma, Algeria.
By using calibration data retrieved from these two methods, raw data values as collected by the sensor (DNs) are converted to Top of Atmosphere (TOA) Reflectance to produce images that are free from sensor and top of atmosphere distortions.